End long waits, overnight antibiogram test done at your veterinary clinic.
Offer the best care to pets and their owners by prescribing the right antibiotic the first time.
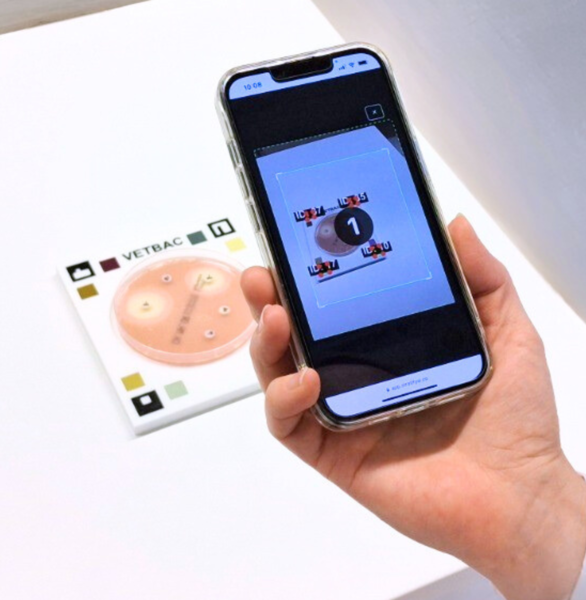

A faster antibiogram test for veterinary clinics
When examining a small animal patient with suspected bacterial infection, veterinarians are faced with a dilemma:
- Do I empirically prescribe an antibiotic today that could work?
- Or do I send in for an antibiogram and wait for 2-7 days before giving a treatment?
There are no good choices here.
That's why we developed VetBac, a faster antibiogram test that provides results on bacterial growth and antibiotic susceptibility in less than 1 day.
End-to-end support for better clinical outcomes
VetBac is not just a test. It's a complete solution providing veterinary clinics with the data and support they need to make evidence-based decisions for antibiotic therapies. It offers:
- A faster antibiogram test
- A clear report with results (cascade-type)
- Rapid access to expert microbiology support
- Access to training and premium learning resources
Who is it for

VetBac is suitable for veterinary clinics treating dogs and cats with infections of skin, ear and urinary tract.
It's ideal for clinics that want to offer the best possible care to pets by reducing the occurrence and consequences of non-improving bacterial infections.
How does it work
The VetBac antibiogram test is a novel solution, bringing together innovation in the development of bacterial culture plates and smart, automated processing of the test results.
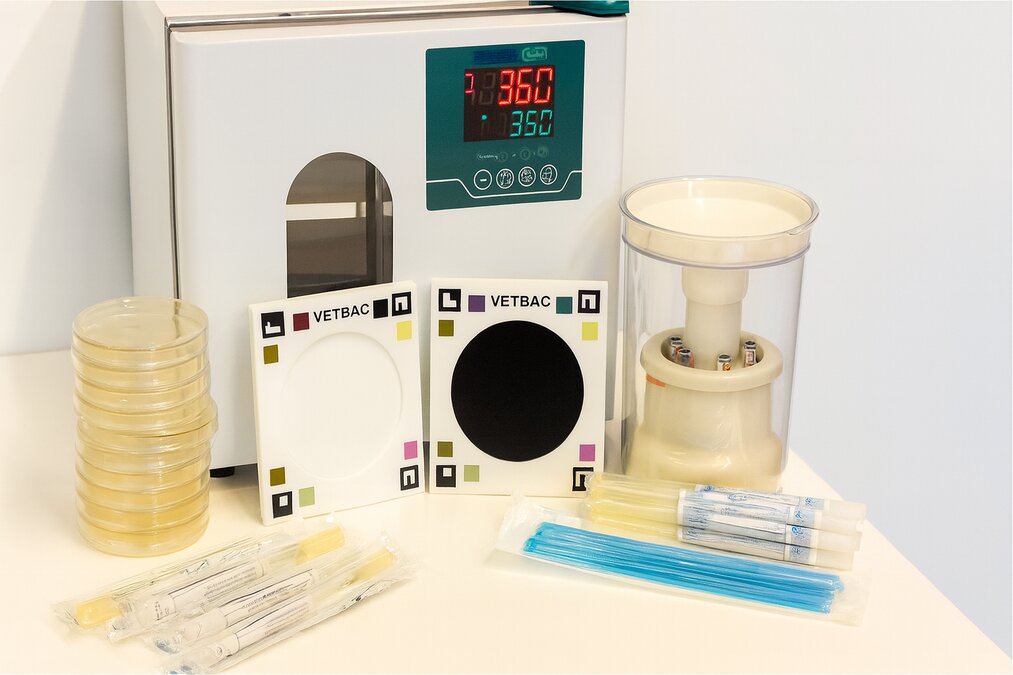
What's included
- incubator
- imaging cards
- disc dispenser
- plates
- antibiotic discs
- swabs & loops
- rapid access to microbiologists for data interpretation and test setup support

The testing protocol
Test setup (2 min)
Inoculate the VetBac plate with the collected sample. Add antibiotic discs.
Incubation (1 min)
Place the inoculated plate in the incubator overnight (16-20 hours).
Capture results (2 min)
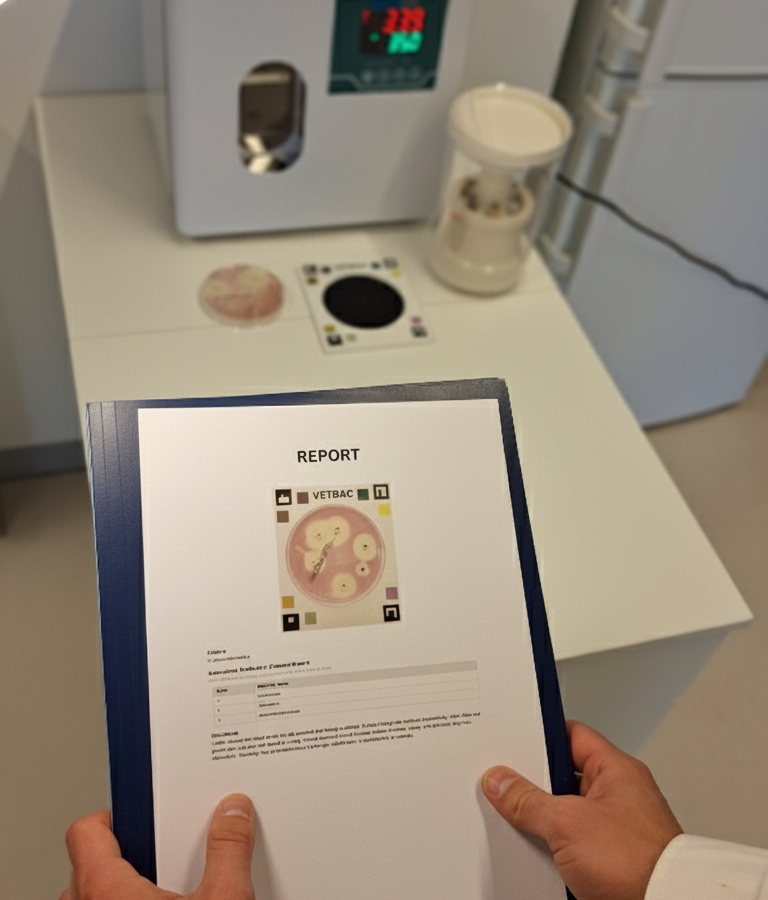
Take a photo of the plate with your smartphone and submit it through the VetBac app.
Get the results (1 min)
Get the advanced AST report (cascade-type) within a few minutes of submission.
Interpretation of results
You'll get a clear, easy-to-understand cascade-type report with the list of susceptible antibiotics to the bacterial infection tested.
You'll also have rapid access to expert microbiology support, in case you want a full report or if antibiogram results conflict with observed clinical signs.
This way, you can always make solid, evidence-based decisions when treating bacterial infections.
Testimonials
"I like that with VetBac, I can access the results as early as the next day. This allows me to quickly determine whether an antibiotic is needed and, if so, which one to choose."
Dr. Urška Vesel
PRVA-K veterinary clinic
Ljubljana, Slovenia
"The VetBac system is easy to use and straightforward to handle. The fast and reliable results are especially impressive and very helpful for clinical decision-making."
Dr. Tjaša Oražem
PET VET veterinary clinic
Ljubljana, Slovenia
About the VetBac team
The VetBac test was developed by an experienced team of veterinarians, microbiology experts, and engineers.
We understand first-hand the difficulties veterinarians face when treating bacterial infections in companion animals.
This is why we created an integrated solution, bringing together a faster antibiogram test and comprehensive support, so that veterinarians can prescribe antibiotics faster and generate better clinical outcomes.
Contact us
If you'd like to find out more about the VetBac solution or see a demo of the product, get in touch by filling the below form. We reply within 1 business day.



